The increasing momentum of India in international space activities makes the ownership questions about space resources more pressing. Space law in India requires urgent development because of the expanding private sector world of space launches, alongside space tourism plans and mining operations on other planets. This article examines the existing legal framework combined with the issues regarding space ownership rights and assesses how India’s space law regulation 2025 aligns itself with global standards.
The Rise of Space Activities in India
Space exploration initiatives in India have produced significant progress through their Mars and lunar missions, and also through their single mission success of launching more than 100 satellites. Indian space exploration was initially ruled by the ISRO legal framework, which focused mainly on government-directed missions. Government efforts to invite private companies into the space sector have introduced a dynamic private space industry in India.
Conflict activity now involves rocket construction along with satellite launch capability, while advancing future space technology development. The Indian space law and policy require changes that will enable proper management of emerging legal questions along with ethical and commercial issues, while private space enterprises develop Earth orbit activities.
Understanding Space Law: Global Foundations
To understand space law in India, it is crucial to first understand its historical development as an international body of knowledge. Five international agreements form the basis of Space law, to which India has officially signed several components. According to the prominent 1967 Outer Space Treaty (OST), all human beings share authority in outer space because it belongs to everyone, and nations cannot claim ownership of space objects.
The Outer Space Treaty, together with comparable international treaties about space, and India fail to establish definitive rules regarding property rights of both private organizations and private citizens in space activities. National legislation supporting private control of space resources has been enacted by the United States and Luxembourg due to the legal uncertainty of the situation. India continues to figure out these space policies using the developing legislation of the India Space Law Regulation 2025 to define its position.
Indian Space Law and Policy: A Growing Framework
The ISRO legal framework functions as a regulatory body to supervise every space mission conducted by India. The national development and scientific progress operated primarily under the direction of the Department of Space (DoS). The framework had limited coverage for commercial business and private industry participation.
After IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) formation in 2020, the Indian government started a complete reform of space laws and policies. The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center serves as a one-stop agency for issuing private space authorization permits while bridging ISRO legal procedures with Indian private space regulations.
The India space Law Regulation 2025 will implement several changes as it approaches adoption and enactment:
- The new law needs to clarify all the responsibilities private operators have in space.
- Introduce regulations for both licensing procedures as well as insurance obligations and liability requirements.
- The regulation must implement responsibility systems for space objects and environmental damage.
- Address ownership, extraction, and utilization of resources from celestial bodies.
The successful definition of space property rights requires consideration of each aspect while complying with both national and international standards.

Space Property Rights: Who Owns the Moon, Mars, and Beyond?
Many jurisdictions maintain an unresolved situation regarding ownership rights concerning space property. Outer space remains a shared domain under international treaties of space and India, since planets and stars, and asteroids do not belong to any nation or private sector.
Lawmakers need to provide prompt solutions addressing this matter. Lunar mining and asteroid resource extraction missions will become practical aims that require answering the ownership question of extracted resources. Even though the OST prohibits space sovereignty claims, it does not specify any restrictions regarding accessing space resources.
The upcoming 2025 India space law regulation will obtain its framework through the adoption of modern concepts from the U.S. Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Act. This law would provide means to use space resources without declaring sovereignty, thus enabling Indian private space sector companies to invest securely.
The Role of ISRO and the Legal Framework
The foundational legal framework of ISRO supports India’s space program, although it functions together with modern regulatory entities. ISRO transforms itself from a single-space operator into a provider of infrastructure and technical support that enables Indian private space sector development.
Private entities became actively involved in Chandrayaan-3 logistics operations as part of a new Indian space industry direction under updated legislation. A cooperative framework between private entities and public organizations will establish itself as the normal practice under the Space Law in India Regulation 2025.
Legal Challenges and Opportunities
The definition of space property rights encounters its main obstacle when national priorities compete with international partnership requirements. India needs to create policies that follow international space agreements as well as national obligations by establishing policies favorable to start-ups and investors.
Another major issue is liability. Private satellite accidents and collisions create the need to determine who bears responsibility under the law. The space law in India regulation 2025 intends to resolve these uncertainties through licensing requirements, which include insurance and liability coverage obligations.
Another role of the regulation will be to handle the following issues:
- The protection of inventions made in space must be established through the intellectual property rights system.
- Data privacy in satellite communication.
- Peaceful space exploration stands in opposition to military functions in outer space.
The implementation of a robust legal system must connect the ISRO legal structure with private space sector requirements throughout India’s entire territory.
International Collaboration and Compliance
The growing international collaboration between India and space agencies creates the necessity for its legal structure to adopt international standards. Violation of international space agreements requires full acceptance and active involvement from India as it works to define new international frameworks.
The 2025 India space law regulation will organize international space cooperation while increasing export restrictions to establish India as a leading responsible space nation. Indian authorities should develop wise plans to protect their strategic position since more nations are joining the Artemis Accords, together with other comparable agreements.
Key Treaties Signed by India in Space Law
| Treaty Name | Year Signed | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Space Treaty (OST) | 1967 | Peaceful use of space |
| Rescue Agreement | 1968 | Astronaut safety |
| Liability Convention | 1972 | Damage compensation |
| Registration Convention | 1976 | Registry of objects in space |
| Moon Agreement | Not Signed | Resource ownership (India has not signed this) |
The Future: A Space-Faring Legal Nation
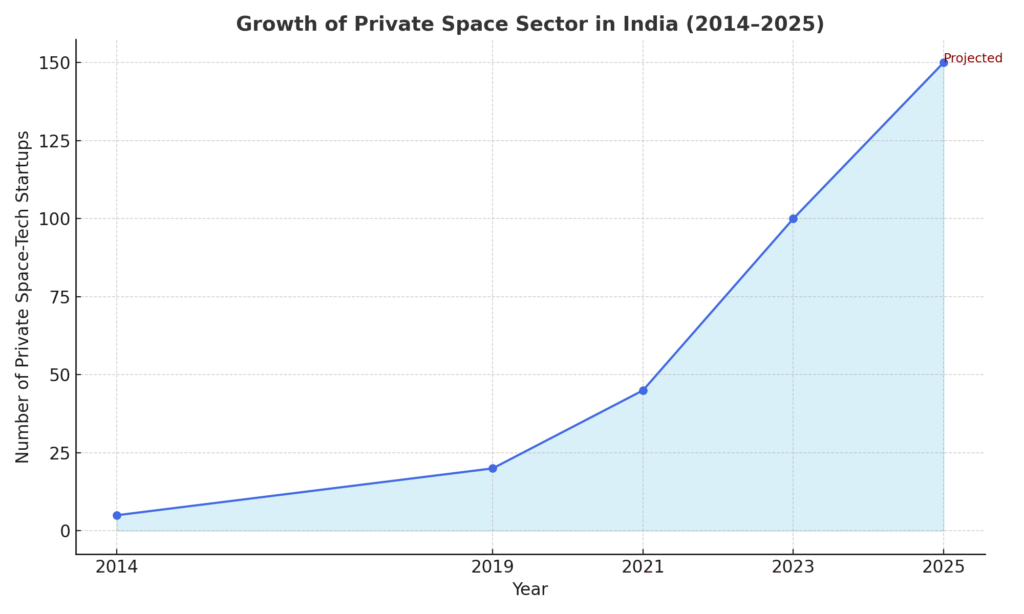
India is ready to be recognized as a major player in the global space industry. The Indian space-tech startup market continues to expand as private space technology enterprises flourish throughout the country. The continuation of this expansion depends on legal certainty.
The India space Law Regulation 2025 provides an essential framework for developing a structured legal system that supports innovation and ensures safety alongside the defense of national interests and adherence to space-related international laws and India’s space obligations.
The ownership issues that exist beyond Earth remain without a definitive solution. A well-balanced space law system in India will establish national leadership in defining the emerging space property rights regime through international standards and progressive perspectives toward future development.
Growth of Private Space Sector in India (2014–2025)
Conclusion
Indian space law demonstrates the national expansion of outer space exploration, together with increasing national obligations in this domain. Each legal advancement between ISRO’s traditional legislations and space law in India regulation 2025 works to build India’s space position through international boundary compliance with international space terms.
The rapid expansion of the Indian private space industry demands direct responses to questions about legal ownership and rights of space resources beyond Earth. The nation stands at an optimal position to graduate from space power status into worldwide leadership of space laws with comprehensive policy backing.
FAQs with Space law in India
- What is Space Law in India?
Space law in India refers to the legal framework that governs activities related to outer space, including satellite launches, space exploration, and commercial space ventures. It is currently guided by ISRO policies and international treaties.
- Can private companies operate in space under Indian law?
Yes, the private space sector in India has been growing rapidly, especially after the creation of IN-SPACe. New laws like the India Space Law Regulation 2025 aim to regulate and promote private participation.
- What legal framework governs ISRO’s operations?
The ISRO legal framework is primarily based on government policies, international agreements, and administrative guidelines. However, with the evolving space ecosystem, formal Indian space law and policy is being drafted to ensure regulatory clarity.
- Does India recognize ownership of space property?
No. As per space property rights under international law, no country or private entity can claim sovereignty or ownership in outer space. India abides by these rules through its participation in international treaties on space and India’s alignment with the Outer Space Treaty.
- What changes are expected from India Space Law Regulation 2025?
The India Space Law Regulation 2025 is expected to introduce clear legal definitions, licensing processes, liability clauses, and promote innovation in the private space sector in India, balancing national interest with commercial growth.



